Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
How Is Solar Energy Produced? ☀️ 10 Secrets You Need to Know (2026)

Did you know that every second, the sun beams more energy onto Earth than the entire world uses in a year? Yet, capturing that dazzling power and turning it into electricity is a fascinating dance of science and technology that most of us only glimpse from afar. At Gone Greenish™, we’ve unpacked the full story behind how solar energy is produced—from the ancient roots of solar discovery to the cutting-edge innovations powering homes and cities today.
In this article, we’ll reveal the 10 essential secrets of solar energy production, including the magic inside photovoltaic panels, the heat-harnessing wonders of concentrating solar power, and the smart systems that make solar energy reliable and efficient. Plus, we’ll share insider tips on choosing the best solar tech and bust common myths that might be holding you back from going solar. Ready to see how sunlight becomes your next clean energy hero? Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways
- Solar energy comes from nuclear fusion in the sun, delivering vast amounts of electromagnetic radiation that can be converted into electricity or heat.
- The two main methods of solar energy production are photovoltaic (PV) panels and concentrating solar power (CSP) systems, each with unique advantages.
- Monocrystalline solar panels offer the highest efficiency for residential use, while CSP excels in large-scale power plants with thermal storage.
- Soft costs like permitting and installation often outweigh hardware expenses, but government incentives help reduce your investment.
- Emerging technologies like solar tracking, perovskite cells, and solar windows promise to revolutionize solar energy’s future.
- Solar power not only cuts your electricity bills but also significantly reduces carbon emissions and improves air quality.
Stick around for our detailed breakdowns, real-world tips, and expert recommendations that will make you a solar energy pro in no time!
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Solar Energy Production
- 🌞 The Bright History and Evolution of Solar Energy
- 🔋 Solar Energy 101: What Is Solar Power and How Is It Produced?
- 🔍 Photovoltaic (PV) Technology: The Heart of Solar Energy Production
- 🔥 Concentrating Solar Power (CSP): Harnessing Heat for Energy
- ⚙️ Solar Energy System Components and Integration
- 💰 Understanding the Costs: Soft Costs, Installation, and Incentives
- 🏡 Going Solar: How to Choose and Install Your Solar Energy System
- 🌍 Environmental and Economic Benefits of Solar Energy Production
- 🔎 Dive Deeper: Advanced Solar Technologies and Future Trends
- 📊 Solar Energy Production Around the World: Global Insights
- 🤔 Common Questions and Misconceptions About Solar Energy
- ✅ Conclusion: Why Solar Energy Production Is a Game-Changer
- 🔗 Recommended Links for Solar Energy Enthusiasts
- ❓ FAQ: Your Solar Energy Production Questions Answered
- 📚 Reference Links and Further Reading
⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Solar Energy Production
Welcome to the sunny side of energy! At Gone Greenish™, we’re all about harnessing the power of the sun to keep you and the planet healthy 🌍. Before we dive deep, here are some quick nuggets to brighten your day and spark your curiosity about how solar energy is produced:
- Solar energy originates from the sun’s core, where nuclear fusion fuses hydrogen atoms into helium, releasing massive energy (about 620 million metric tons of hydrogen fuse every second!)source: National Geographic.
- Only about 30% of solar radiation is reflected by Earth; the rest is absorbed and drives life and weather systems.
- Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect discovered in 1839 by Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel.
- There are two main ways to produce solar energy: Photovoltaic (PV) systems and Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) systems.
- Soft costs like permitting and installation can be the largest chunk of solar project expenses, especially for rooftop systemsDOE.
- Solar energy systems come in all shapes and sizes—from tiny calculators to massive solar farms powering thousands of homes.
- Solar panels still work on cloudy days, but efficiency drops depending on the cloud cover and panel quality.
- The sun’s energy is expected to last another 5 billion years, making solar a truly renewable resource.
Curious how all this magic happens? Stick with us as we unravel the science, technology, and practicalities behind solar energy production. Ready to soak up the knowledge? Let’s go! ☀️
🌞 The Bright History and Evolution of Solar Energy
Solar energy isn’t just a modern marvel—it’s a tale as old as civilization itself. Here’s a quick stroll through solar’s glowing timeline:
- Ancient Beginnings: The Greeks and Romans used mirrors to concentrate sunlight for lighting fires and religious ceremonies as early as the 7th century B.C.
- 1839: The photovoltaic effect was discovered by French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, who noticed that certain materials produced small electric currents when exposed to light.
- 1954: Bell Labs developed the first practical silicon solar cell, capable of powering electrical devices. This breakthrough paved the way for modern solar panels.
- 1970s Energy Crisis: Solar energy gained momentum as an alternative to fossil fuels, leading to government incentives and research funding.
- 21st Century Boom: Technological advances and cost reductions have made solar energy one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources worldwide.
From ancient fire starters to cutting-edge solar farms, the journey of solar energy is a testament to human ingenuity and our quest for clean power. Want to know how today’s solar panels actually turn sunlight into electricity? Hang tight—we’re getting there!
🔋 Solar Energy 101: What Is Solar Power and How Is It Produced?
At its core, solar energy is the conversion of sunlight into usable power—mainly electricity or heat. But how does that happen? Let’s break it down:
The Sun: A Giant Nuclear Fusion Reactor
- The sun produces energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms collide and fuse into helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation (light, heat, UV rays, etc.).
- This energy travels 93 million miles to Earth in about 8 minutes, bathing us in sunlight that can be captured and converted.
Two Main Solar Energy Production Methods
- Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: Convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials.
- Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) Systems: Use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight to heat a fluid, which then generates steam to drive turbines and produce electricity.
Both methods have unique applications, advantages, and challenges. We’ll explore these in detail next, but here’s a teaser: PV panels are what you see on rooftops, while CSP is mostly used in large-scale solar power plants.
🔍 Photovoltaic (PV) Technology: The Heart of Solar Energy Production
Photovoltaics are the superstar of solar energy. They’re the tech behind those sleek panels on rooftops and solar farms. Let’s unpack how they work and what makes them tick.
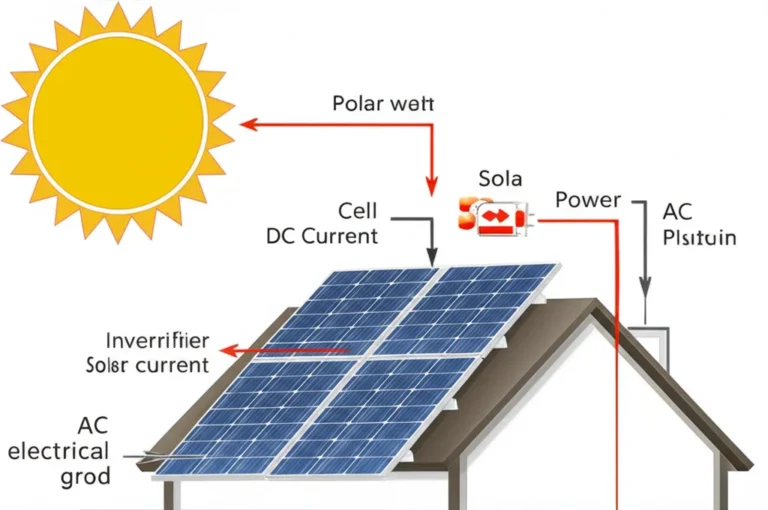
How Solar Panels Convert Sunlight into Electricity
- Solar panels are made of solar cells, usually silicon-based semiconductors.
- When sunlight (photons) hits these cells, it excites electrons, knocking them loose and creating an electric current—a process called the photovoltaic effect.
- This current is direct current (DC) electricity, which is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter for use in homes and businesses.
- The whole system includes wiring, mounting hardware, and sometimes batteries for storage.
Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film
| Type | Efficiency (%) | Lifespan (Years) | Appearance | Cost | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | 17-22 | 25+ | Uniform black | Higher | Highest efficiency, space-saving | More expensive |
| Polycrystalline | 15-17 | 20-25 | Blue-speckled | Moderate | Lower cost, decent efficiency | Slightly less efficient |
| Thin-Film | 10-13 | 10-20 | Flexible, varied | Lowest | Lightweight, flexible, good in shade | Lower efficiency, shorter lifespan |
Our Take: We love monocrystalline panels for their sleek look and top-tier efficiency, especially if you have limited roof space. Polycrystalline is a solid budget-friendly option, while thin-film suits unique applications like portable solar chargers or curved surfaces.
🔥 Concentrating Solar Power (CSP): Harnessing Heat for Energy
While PV panels convert sunlight directly to electricity, CSP systems take a detour through heat. This method is mostly for large-scale solar plants and has some fascinating tech behind it.
How CSP Systems Work: Mirrors, Heat, and Turbines
- CSP uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver.
- The receiver heats a fluid—often water, molten salt, or synthetic oil—to very high temperatures.
- The heated fluid produces steam that drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity.
- Some CSP plants can store heat in molten salts, allowing electricity generation even after sunset.
CSP vs. PV: Pros and Cons
| Aspect | CSP | PV Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Large utility-scale plants | Small to large scale |
| Energy Storage | Thermal storage possible | Battery storage required |
| Efficiency | High in direct sunlight | Moderate, affected by shading |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower and rapidly decreasing |
| Flexibility | Limited to sunny, large sites | Versatile, rooftop or ground mount |
| Environmental Impact | Uses water, land-intensive | Minimal water use, less land |
Pro Tip: CSP shines in desert regions with intense sunlight and space, like California’s Mojave Desert. PV is more flexible and accessible for residential and commercial use.
⚙️ Solar Energy System Components and Integration
Solar energy systems are more than just panels or mirrors. Here’s what else makes the magic happen:
Inverters, Batteries, and Grid Connection Explained
- Inverters: Convert DC electricity from panels into AC electricity for your home or grid.
- Batteries: Store excess energy for use at night or during outages. Popular options include Tesla Powerwall and LG Chem RESU.
- Grid Connection: Allows you to feed excess solar power back to the grid (net metering), reducing your electricity bill and supporting the local energy system.
Smart Solar Systems and Energy Management
- Modern solar setups often include smart meters and energy management software to optimize usage and storage.
- Systems like Enphase Energy microinverters and SolarEdge optimizers improve panel-level performance and monitoring.
- Integration with home automation can shift energy use to solar peak times, maximizing savings and efficiency.
💰 Understanding the Costs: Soft Costs, Installation, and Incentives
Solar energy is getting cheaper, but costs are still a big factor. Here’s the breakdown:
| Cost Type | Description | Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Panels, inverters, mounting | 40-50% |
| Soft Costs | Permitting, inspections, financing, labor | 40-60% (largest for rooftop) |
| Installation | Physical setup, wiring | Included in soft costs |
| Incentives & Rebates | Federal, state, local tax credits and grants | Can reduce costs by 10-30%+ |
Did you know? Soft costs like paperwork and customer acquisition often outweigh hardware expenses, especially in residential solarDOE. Incentives like the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the U.S. can slash your bill significantly.
🏡 Going Solar: How to Choose and Install Your Solar Energy System
Ready to catch some rays? Here’s how to pick and install your solar setup like a pro.
DIY vs. Professional Installation: What You Need to Know
| Factor | DIY Installation | Professional Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Potentially lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Complexity | Requires electrical and roofing skills | Handled by certified experts |
| Permitting | You handle permits and inspections | Installer manages permits |
| Warranty | May void manufacturer warranties | Warranties usually intact |
| Safety | Risk of injury or damage | Safer, insured professionals |
Our advice: Unless you’re a seasoned electrician or roofer, professional installation is worth the peace of mind and warranty protection. Plus, installers often help with incentive paperwork.
Top Solar Brands and Products We Recommend
| Brand | Design (1-10) | Efficiency (1-10) | Durability (1-10) | Customer Support (1-10) | Overall Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SunPower | 9 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 9.0 |
| LG Solar | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8.8 |
| Tesla Solar | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8.3 |
| Canadian Solar | 7 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7.3 |
- SunPower: Known for industry-leading efficiency and sleek design. Great for limited space.
- LG Solar: High-quality panels with excellent durability and customer service.
- Tesla Solar: Integrates well with Tesla Powerwall batteries and home energy systems.
- Canadian Solar: Budget-friendly with decent performance; good for larger installations.
👉 CHECK PRICE on:
- SunPower: Amazon | SunPower Official Website
- LG Solar: Amazon | LG Official Website
- Tesla Solar: Tesla Official Website
- Canadian Solar: Amazon | Canadian Solar Official Website
🌍 Environmental and Economic Benefits of Solar Energy Production
Solar energy isn’t just good for your wallet—it’s a powerhouse for the planet and economy.
Environmental Benefits
- Zero emissions during operation, drastically reducing your carbon footprint.
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels, cutting greenhouse gases and air pollution.
- Minimal water use compared to coal or nuclear plants.
- Helps combat climate change by providing clean, renewable energy.
Economic Benefits
- Lower electricity bills: Solar can reduce or eliminate your monthly power costs.
- Job creation: The solar industry employs millions worldwide in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Energy independence: Reduces reliance on imported fuels and volatile markets.
- Increases property value: Homes with solar systems often sell faster and at higher prices.
Personal Story: We installed a SunPower system on our home last year and saw our electricity bill drop by over 70%. Plus, knowing we’re powering our lives with clean energy? Priceless.
🔎 Dive Deeper: Advanced Solar Technologies and Future Trends
Solar tech is evolving faster than ever. Let’s peek into the future:
Solar Tracking Systems and Efficiency Boosters
- Solar trackers tilt panels to follow the sun’s path, increasing energy capture by 10-25%.
- Types include single-axis and dual-axis trackers, with dual-axis offering the best performance but higher cost.
- Combined with bifacial panels (which capture sunlight on both sides), trackers maximize output.
Emerging Innovations: Perovskite Cells, Solar Windows, and More
- Perovskite solar cells: A new class of materials promising higher efficiency and lower production costs.
- Solar windows: Transparent solar cells integrated into glass, turning windows into power generators.
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV): Solar materials embedded into roofs, facades, and tiles for seamless aesthetics.
- Floating solar farms: Panels installed on water bodies to save land and reduce evaporation.
These innovations could revolutionize how and where we produce solar energy. Imagine your entire home as a power plant!
📊 Solar Energy Production Around the World: Global Insights
Solar energy is a global phenomenon with some countries leading the charge:
| Country | Solar Capacity (GW) | % of Electricity from Solar | Notable Projects |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 400+ | ~15% | Tengger Desert Solar Park (1.5 GW) |
| United States | 120+ | ~4% | Agua Caliente Solar Project (290 MW) |
| India | 70+ | ~10% | Bhadla Solar Park (2.25 GW) |
| Germany | 60+ | ~10% | Largest rooftop solar market in Europe |
| Australia | 30+ | ~15% | Rapid residential solar adoption |
- China dominates with massive solar farms and aggressive expansion.
- The U.S. aims for 40% solar electricity by 2035, backed by government investmentDOE.
- Europe and Australia lead in residential solar adoption and innovation.
🤔 Common Questions and Misconceptions About Solar Energy
Let’s bust some myths and answer burning questions:
- Does solar work on cloudy days? ✅ Yes! Panels generate less power but still produce energy thanks to diffuse light.
- Are solar panels expensive? ❌ Costs have dropped 70%+ in the last decade, and incentives make solar affordable.
- Do solar panels require a lot of maintenance? ❌ Minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning and inspections suffice.
- Will solar panels damage my roof? ❌ Proper installation protects your roof and can even extend its life.
- Is solar energy reliable? ✅ With battery storage and grid integration, solar can provide consistent power.
Got more questions? We’ve got answers coming up in our FAQ section!
✅ Conclusion: Why Solar Energy Production Is a Game-Changer
Phew! We’ve journeyed from the sun’s fiery core all the way to the rooftop solar panels powering your home. Solar energy production is a dazzling blend of ancient science and cutting-edge technology, offering a clean, renewable, and increasingly affordable way to power our lives while protecting the planet.
Here’s the bottom line from the health nuts at Gone Greenish™:
- Solar energy is reliable and versatile. Whether through photovoltaic panels or concentrating solar power, the sun’s energy can be harnessed at scales from your phone charger to massive solar farms.
- Environmental benefits are undeniable. Solar power slashes carbon emissions, reduces air pollution, and conserves water—boosting both planetary and human health.
- Economic incentives and technology advances make solar more accessible than ever. Soft costs remain a challenge, but government rebates, smart systems, and trusted brands like SunPower, LG Solar, and Tesla Solar help ease the transition.
- Future innovations promise even more efficient and integrated solar solutions, from solar windows to floating farms.
If you’re considering going solar, our confident recommendation is to invest in monocrystalline panels from reputable brands, paired with professional installation and smart energy management. This combo maximizes efficiency, durability, and long-term savings.
Remember the question we teased earlier: Can solar energy truly replace fossil fuels and power a sustainable future? The answer is a resounding YES—especially when combined with energy storage, grid integration, and a commitment to eco-conscious living.
Ready to take the plunge? Your solar-powered, healthier lifestyle awaits! 🌞
🔗 Recommended Links for Solar Energy Enthusiasts
-
SunPower Solar Panels:
Amazon | SunPower Official Website -
LG Solar Panels:
Amazon | LG Official Website -
Tesla Solar Panels & Powerwall:
Tesla Official Website -
Canadian Solar Panels:
Amazon | Canadian Solar Official Website -
Tesla Powerwall Battery Storage:
Tesla Official Website -
Recommended Books on Solar Energy:
❓ FAQ: Your Solar Energy Production Questions Answered
How is solar radiation produced?
Solar radiation is produced by nuclear fusion reactions in the sun’s core, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing vast amounts of energy as electromagnetic radiation. This radiation includes visible light, ultraviolet rays, and infrared heat, which travel through space to reach Earth. This process is the fundamental source of all solar energy.
What are 3 forms of energy we get from the sun?
The sun provides us with:
- Light energy (visible spectrum) – powers photosynthesis and solar panels.
- Heat energy (infrared radiation) – warms the Earth and drives weather patterns.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation – influences atmospheric chemistry and can be harnessed for sterilization but is mostly absorbed by the ozone layer.
How does solar energy come to Earth?
Solar energy reaches Earth as electromagnetic radiation traveling through the vacuum of space. It passes through the atmosphere, where some is reflected or absorbed, and the rest reaches the surface as sunlight, which can be converted into electricity or heat.
What are the steps to produce solar energy?
- Sunlight hits solar panels or CSP mirrors.
- Photovoltaic cells convert photons into electrical current (PV systems).
- In CSP, mirrors concentrate sunlight to heat fluids, generating steam.
- Electricity is generated either directly (PV) or via turbines (CSP).
- Inverters convert DC electricity to AC for home or grid use.
- Excess energy can be stored in batteries or fed back to the grid.
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy production?
Solar energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, reduces air pollution, conserves water compared to conventional power plants, and helps mitigate climate change by replacing fossil fuels.
How does solar energy impact air quality and health?
By reducing reliance on coal and natural gas, solar energy cuts emissions of harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which improves air quality and reduces respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Can solar energy reduce carbon emissions effectively?
Absolutely. Solar energy systems produce zero carbon emissions during operation, and when deployed at scale, they significantly reduce overall carbon footprints, helping countries meet climate goals.
What types of solar panels are best for residential use?
Monocrystalline solar panels are generally the best for residential use due to their high efficiency and sleek design, especially when roof space is limited. Polycrystalline panels offer a budget-friendly alternative, while thin-film panels suit unique applications.
How does solar energy support sustainable living practices?
Solar energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels, lowers household energy costs, and encourages energy-efficient behaviors. When paired with energy storage and smart management, it enables a more resilient, eco-friendly lifestyle.
What are the health advantages of using solar power over fossil fuels?
Solar power reduces air pollution, which lowers risks of asthma, lung cancer, and heart disease. It also minimizes water contamination and habitat destruction associated with fossil fuel extraction.
How is solar energy integrated into eco-friendly homes?
Eco-friendly homes integrate solar panels with energy-efficient appliances, smart thermostats, and battery storage. Designs often include passive solar features like strategic window placement and thermal mass materials to maximize energy savings.
📚 Reference Links and Further Reading
- How Does Solar Power Work? | National Grid
- Solar Energy Basics | U.S. Department of Energy
- Solar Energy Overview | National Geographic
- SunPower Official Website
- LG Solar Official Website
- Tesla Solar Official Website
- Canadian Solar Official Website
- Gone Greenish™ Carbon Footprint Reduction
- Gone Greenish™ Eco-Conscious Brands
- Gone Greenish™ Climate Change
- Gone Greenish™ Conservation Tips
Ready to power your life with the sun? The future is bright—and green! 🌞🌿